A surge of new attacks by an Islamic State-affiliated group in Mozambique’s Cabo Delgado province has left more than 70 children missing, with fears they may have drowned in a river or been kidnapped by militants as thousands of families fled, local authorities and a group of aid agencies said.
Around 30 families now seeking shelter in Nampula province to the south have asked police to help locate their children, according to a report released Wednesday by the Protection Working Group, a network of non-governmental organizations and United Nations agencies.
The attacks have hit areas that had been relatively untouched since the start of the jihadist insurgency in Cabo Delgado in 2017. They may mark a new stage in a crisis that aid agencies say forced more than a million people to flee their homes during nearly seven years of violence. Thousands were killed.
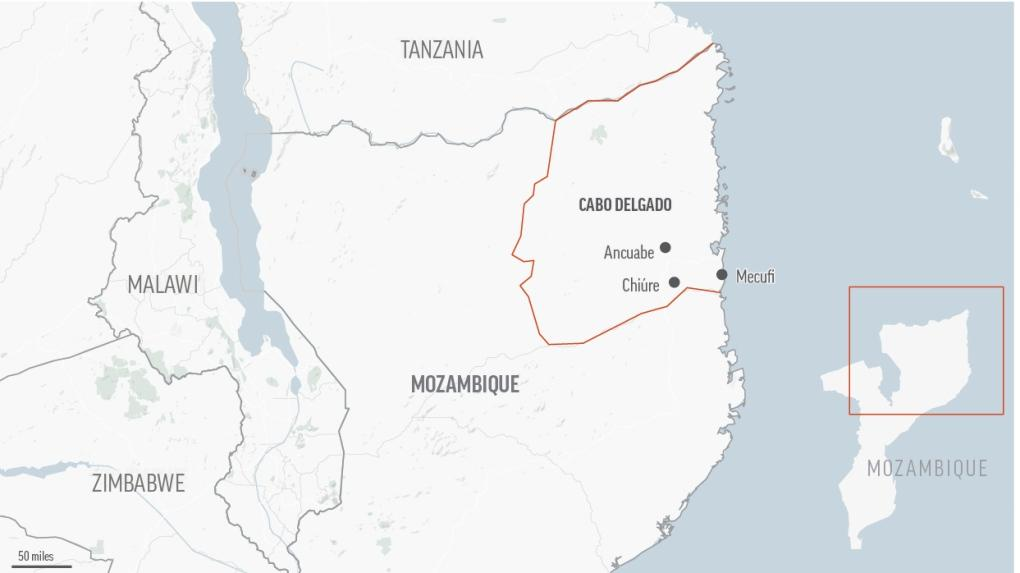
Cabo Delgado, Mozambique’s northernmost province that borders Tanzania, was thrust into the international spotlight in 2020 and 2021 when insurgents were accused of carrying out mass beheadings, including of children.
The U.N.’s migration agency said nearly 100,000 people were displaced between early February and early March after Islamic State Mozambique fighters launched a new offensive from their heartland in coastal central Cabo Delgado into the south. More than 61,000 of those displaced were children, it said.
Save the Children called it the largest displacement of children in Cabo Delgado in 18 months.
“There are repeated reports of beheadings and abductions, including multiple child victims,” Save the Children said.
The U.N. high commissioner for refugees, Filippo Grandi, is in Cabo Delgado and was due to update on the situation and humanitarian response on Thursday.
A total of 72 children have now been reported missing after the recent attacks, said Albertina Ussene, the Nampula provincial government’s director of gender, children and social action, who was quoted by the Lusa news agency. Ussene told a meeting of provincial officials this week that another 29 children had been reunited with their families.
The report by the Protection Working Group said around 27 villages in southern Cabo Delgado were attacked late last month. It said children and older people were reported to have drowned while trying to escape, and some men were believed to have been kidnapped.
The report said an unconfirmed number of people were killed and 500 buildings, including houses, churches and markets, were destroyed.
The U.N. children’s agency said the displacement of tens of thousands more people risks exacerbating cholera outbreaks due to overcrowding and the lack of clean water and sanitary facilities in displacement sites.
Insurgent attacks were relatively limited in Cabo Delgado last year. The head of the Mozambique army, Maj. Gen. Tiago Nampele, said in December that the troubled province was “90-95 per cent secure.”
But over the weekend, Islamic State Mozambique fighters occupied the coastal town of Quissanga, one of Cabo Delgado’s district capitals, which the Mozambican military had left unprotected. The next day, insurgents beheaded three members of the security forces on a nearby island.
The army’s ability to stop the killings has long been questioned.
Mozambique has been fighting the jihadist militants in the north since October 2017. Initially known as Ansar al-Sunna, the insurgent group affiliated with Islamic State in 2019. It is composed mostly of Mozambicans with some fighters coming from Tanzania and further abroad.
Islamic State Mozambique’s political goals have not been explicitly stated, but it recently made attempts to impose Islamic law in areas under its influence.
Piers Pigou, the head of southern Africa at the Institute for Security Studies, said the recent mass displacements showed how fragile security in Cabo Delgado remains.
“The government acknowledges that only a handful of insurgents can generate widespread uncertainty,” he said. “This will not change unless communities have far greater belief that the security forces will be able to provide the required stability.”