Report implicates Wagner group fighters in Moura atrocity, including the torture and rape of civilians
First came a single helicopter, flying low over the marshes around the river outside the village, then the rattle of automatic fire scattered the crowds gathered for the weekly market.
Next came more helicopters, dropping troops off around the homes and cattle pens. The soldiers moved swiftly, ordering men into the centre of the village, gunning down those trying to escape. When some armed militants fired back, the shooting intensified. Soon at least 20 civilians and a dozen alleged members of an al-Qaida affiliated Islamist group, were dead.
Over the next five days, hundreds more would die in the village of Moura in the Mopti region of Mali at the hands of troops overseen by Russian mercenaries, according to a new United Nations report. All but a small fraction were unarmed civilians.
Published last week after an extensive human rights fact-finding mission conducted over several months by UN staff in Mali, the report gives an hour by hour account of events during a five-day military operation in Moura in March 2022, giving details of the worst single atrocity associated with the Kremlin-linked Wagner group outside Ukraine.
Investigators from the UN human rights office concluded that there are strong indications that more than 500 people were killed – the majority in extrajudicial killings – by Malian troops and foreign military personnel believed to be from Wagner, a mercenary outfit run by Yevgeny Prigozhin, a close ally of the Russian president, Vladimir Putin, which was linked to the massacre by internal messages obtained by the Guardian last year.
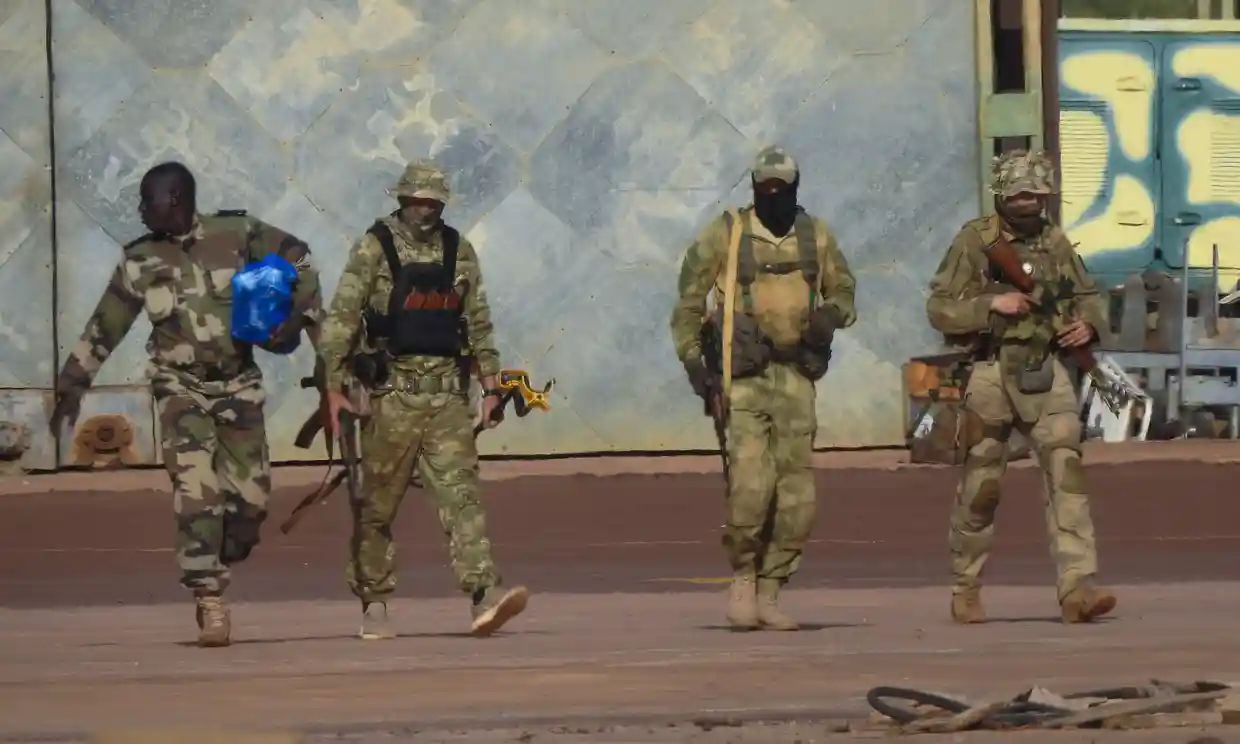
The new allegations again underline the extent of human rights abuses blamed on Wagner, which has also operated in at least six other African countries as well as Libya and Syria.
In recent months, Wagner fighters have spearheaded the Russian push to seize the Ukrainian city of Bakhmut, which has been fiercely contested by Kyiv’s forces, and suffered heavy casualties. Wagner has been accused of involvement in multiple massacres in Mali as well as elsewhere in the Sahel and central Africa. Witnesses say the group has been caught up in fierce fighting in Central African Republic in recent months.
As France and the US have shifted resources and attention away from Africa in recent years, Russia has moved to fill the gap, mounting a series of diplomatic offensives and using Wagner to win over regimes in key states by offering to bolster weak security forces against enemies ranging from Islamist extremists to pro-democracy domestic opposition parties.
Western officials allege the Kremlin is using Wagner to advance Russian economic and political interests across Africa and elsewhere. The effort is backed by an extensive disinformation campaign, they say.
Analysts have recorded a surge in violence wherever Wagner has deployed, although rarely with much military success for governments. Last month, at least nine civilians were killed and more than 60 injured in a triple suicide bomb attack in the central Mali town of Sévaré early on a Saturday, an official has said.
When the Russian mercenaries were hired in Mozambique in 2019 to fight Islamist militants there, they were forced to withdraw after suffering heavy casualties. Eventually, Rwandan regular troops were flown in, successfully countering the insurgents’ offensive.
Few of the atrocities alleged to have involved Wagner have been conclusively linked to the group, however. A lack of witnesses, resistance from local regimes, poor infrastructure and acute insecurity have made full investigation of claims difficult.
The Moura massacre is an exception, however. “These are extremely disturbing findings,” said Volker Türk, the UN high commissioner for human rights. “Summary executions, rape and torture during armed conflict amount to war crimes and could, depending on the circumstances, amount to crimes against humanity.”
Malian authorities denied requests by the team to access Moura itself but the report is based on interviews with victims and witnesses, as well as forensic and other information sources, such as satellite imagery.
Mali’s elected president, Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta, was toppled in August 2020 by officers angered at the failures to roll back the jihadist insurgency. In 2021, the military forced out an interim civilian government and tilted dramatically towards Moscow, concluding an agreement in which about 1,000 fighters from the Wagner group were deployed to bases across much of the country, which also received consignments of Russian weapons.
A Malian government spokesperson described the report as “biased” and “based on a fictional account”, and said an investigation by Malian judicial authorities had found “not a single civilian in Moura was killed during the military operation”, only “armed terrorists”.
The operation – described by the authorities as an anti-terrorist military operation against an Islamist extremist group, Katiba Macina, which has imposed its rigorous and intolerant version of sharia law on inhabitants, raised taxes and made local men follow their dress codes – began on 27 March 2022, a busy market day in Moura.
The accounts gathered by the UN support the testimony of witnesses who spoke to reporters last year. Amadou Barry, who lives in the neighbouring village, told the Observer he was attending the market in Moura when helicopters suddenly appeared and troops disembarked, prompting a small group of Islamist militants in the village to shoot at the soldiers before fleeing on motorbikes.
“We started running in every direction, some into the houses. The Malian army then opened fire on people running, killing so many people,” he said.
Then, over the next four days, at least 500 people are believed to have been killed, says the report, which names at least 238 of these victims.
Héni Nsaibia, senior researcher at ACLED (Armed Conflict Location and Event Data Project), said in the weeks after the massacre that between 60 and 100 of those killed may have been unarmed Islamist militants, but the rest were civilians. Government forces found large quantities of weapons in Moura.
Witnesses reported seeing “armed white men” who spoke an unknown language operating alongside the Malian forces and at times appearing to supervise operations, the report found. It cites witnesses who claimed Malian troops were rotated in and out of Moura daily, but the foreign personnel remained.
Internal Malian army documents obtained by the Guardian last year revealed the presence of Wagner fighters – referred to as “Russian instructors” – on “mixed missions” with Malian soldiers and gendarmes around the time of the Moura massacre. Wagner were deployed near Moura at the time, and took part in other operations in which many civilians were killed.
According to the new report, on the day after the initial assault soldiers began going house to house searching for “presumed terrorists”, selecting and killing people with long beards, people wearing ankle-length trousers (a sign of religious devotion), people with marks on their shoulders – seen as evidence of firing or carrying weapons – and even those who merely showed signs of fear.
A group of men rounded up in the south-east of the village were led away by soldiers and shot in the head, back or chest, and their bodies thrown into a ditch. Witnesses said that those who resisted or tried to flee were also executed by the Malian armed forces and the “armed white men” and dumped into the ditch.
Detainees were subjected to torture and other ill-treatment during questioning, and dozens of women and girls were raped or subjected to other forms of sexual violence, the report claims. In one instance, soldiers brought bedding from a house, placed it under trees in the garden, and took turns raping women they had forced there.
Samira Daoud, Amnesty International’s regional director for west and central Africa, said what happened in Moura could constitute crimes under international law.
“While the [UN] notes that around 30 combatants from the armed group Katiba Macina were present in Moura on 27 March 2022 … their presence can in no way justify the extrajudicial executions, rapes and looting committed by the armed forces against the inhabitants and stallholders trapped by their siege,” Daoud said.
Analysts have expressed concerns that the recent crisis in Sudan has distracted attention from deepening problems across the Sahel, an unstable belt of desert and grazing running east from Senegal across the African continent. The zone is afflicted by extreme weather linked to climate change, displacement of millions of people, acute political instability and growing violence. Analysts fear the conflict in Sudan may lead to a “domino” effect of state collapse.